Diese Wiki-Seite dient zum Sammeln von Informationen, wie Nachhaltigkeitsaspekte in die Lehre in den Studiengängen Informatik, Softwaretechnik und Data Science integriert werden könnten. Hierzu lohnt sich insbesondere der Blick auf andere Hochschulen.
Aktueller Stand
Definition "Nachhaltigkeit in der Informatik"
Es gibt keine einheitliche Definition, was Nachhaltigkeit in der Informatik bedeutet. Nachfolgend ein paar Konzepte, die jeweils versuchen, Nachhaltigkeit in Bezug zu Informatik bzw. Informationstechnik zu definieren...
5 Domains by Karlskrona Manifesto
Visualization by Luís Cruz.
Karlskrona Manifesto: C. Becker et al. (2015). Sustainability Design and Software: The Karlskrona Manifesto. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSE.2015.179 ↩
TING-D
Nachhaltigkeitsverständnis TING-D: Nachhaltigkeit in Bezug auf Technik, Individuum, Natur, Gesellschaft und Demokratie (Inspiration durch #gnuHU):
- Technische Nachhaltigkeit: Freie Software, offene Protokolle, ...
- Individuelle Nachhaltigkeit: Datenschutz, Datensouveränität, Autonomie des Users, ...
- Naturbezogene / ökologische Nachhaltigkeit: Energieeffizienz, digitale Suffizienz, Nutzung erneuerbarer Energien, ...
- Gesellschaftliche Nachhaltigkeit: Unterstützung von zivilgesellschaftlichem Engagement, demokratische Partizipation, ...
- Demokratische Nachhaltigkeit: Veränderungen an der Software ist durch alle möglich, Zusammenarbeit ermöglichen, ...
Tech Doughnut
Der Tech Doughnut ist inspiriert durch das Modell der Donut-Ökonomie von Kate Raworth.
Seven ways to transform our thinking and imagination, from the old economic thinking of the 20th century, to the thinking we will need to guide us towards a new goal for humanity:
KIF500: Resolution Nachhaltigkeitsaspekte in der Lehre
Verabschiedet am 29. Mai 2022
https://wiki.kif.rocks/wiki/KIF500:Resolutionen/Nachhaltigkeitsaspekte_in_der_Lehre
Die 50,0. Konferenz der deutschsprachigen Informatikfachschaften fordert, einen stärkeren Fokus auf Nachhaltigkeit im Informatikstudium zu legen.
Studierende sollten sich im Laufe ihres Studiums mit den Folgen der erlernten Technologien mit Bezug auf die Klimakrise auseinandersetzen.
- Studierende als (zukünftige) Informatiker:innen sollen sich ihrer Verantwortung für Klimagerechtigkeit bewusst sein, vor allem als Teil des Globalen Nordens [1].
- Studierende müssen sich in ihrem Arbeitsalltag und auch jetzt schon mit der Klimakrise und ihren Auswirkungen beschäftigen.
Die KIF fordert, mindestens ein Nachhaltigkeitsmodul im Bachelor-Studium einzurichten. Weiterhin sollen vielfältige Nachhaltigkeitsaspekte in allen Modulen eingebunden werden, in denen es sinnvoll möglich ist.
Lehrangebote mit Nachhaltigkeitsbezug an der Universität Stuttgart
| Name | Art | Umfang | Inhalte | Anmerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computerethik | Fachübergreifende Schlüsselqualifikation | 3 LP | Zunächst werden die Grundprinzipien der Ethik dargelegt, wie sie für die Betrachtung der Computer-Ethik von besonderer Bedeutung sind. Anschließend wird anhand von Fallbeispielen/-studien demonstriert, unter welchen ethischen Gesichtspunkten Problemstellungen des Einsatzes von Computern behandelt werde können. Die Beispiele stammen aus dem Bereich der Medizin, der Technik sowie des täglichen Lebens | Mitwirkende:
|
Lehrangebote mit Nachhaltigkeitsbezug an anderen Hochschulen
| Name | Hochschule | Verpflichtend? Wahlmodul? | Umfang | Inhalte | Anmerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ways of Thinking in Informatics | TU Wien | Informatik-Studierende im ersten Bachelor-Jahr | 6 LP |
| |
| Sustainable Technology | Hochschule Trier |
| |||
| Nachhaltige Softwaretechnik | Umwelt-Campus Birkenfeld (Hochschule Trier) | Wahlmodul | 5 ECTS |
| Dozent: Prof. Dr. Stefan Naumann Teil der Vertiefungsrichtung Sustainability and Information Systems |
| Nachhaltigkeit und IT | Uni Würzburg | Pflicht für Studierende des Bachelor-Studiengangs "Informatik und Nachhaltigkeit" | 5 ECTS |
| Dozent: Stefan Wunderer |
| Energy-Aware Engineering | Uni Würzburg | 5 ECTS |
| ||
| Systems Benchmarking | Uni Würzburg | Wahlfach im Master Informatik | 5 ECTS |
| Dozent: Prof. Samuel Kounev |
| Technik und Ethik | TU Graz | Pflicht für Studierende des Studiengangs "Information and Computer Engineering" | 2 ECTS | In der Lehrveranstaltung werden soziale, ethische und rechtliche Aspekte des Informations- und Computer Engineerings thematisiert. Nach einer generellen Einführung in ethische Theorien zu Technik fokussiert die Lehrveranstaltung auf zentrale ethische und rechtliche Herausfordungen von ICE. Anhand von Fallbeispielen werden aktuelle Fragestellungen, Konflikte und öffentliche Debatten sowie Normsetzungprozesse diskutiert. | |
| Green Software Engineering | University of Minho | Wahlmodul im Master-Programm Software Engineering | Objectives:
| Siehe Paper: Saraiva, J., Zong, Z., & Pereira, R. (2021). Bringing Green Software to Computer Science Curriculum: Perspectives from Researchers and Educators. Proceedings of the 26th ACM Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education V. 1, 498–504. https://doi.org/10.1145/3430665.3456386 | |
| Texas State University | Wahlmodul im Ph.D.-Programm Computer Science | Objectives:
| Siehe Paper: Saraiva, J., Zong, Z., & Pereira, R. (2021). Bringing Green Software to Computer Science Curriculum: Perspectives from Researchers and Educators. Proceedings of the 26th ACM Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education V. 1, 498–504. https://doi.org/10.1145/3430665.3456386 | ||
| Service Oriented Design | Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam | Bei Wahl der Vertiefungsrichtung "Software Engineering and Green IT" verpflichtend | 6 ECTS |
| |
| Green Lab | Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam | Bei Wahl der Vertiefungsrichtung "Software Engineering and Green IT" verpflichtend | 6 ECTS |
| |
| OpenHPI-Kurse (MOOCs) zu Clean-IT | Hasso-Plattner-Institut Potsdam | Freiwillig | Kurse: Das HPI rechnet seinen Studierenden dafür ECTS-Punkte (European Credit Transfer System) an und empfiehlt dies auch anderen Hochschulen. | ||
| Seminar "Green Computing and Sustainability" | University at Buffalo | Wahlmodul | We will read and discuss state-of-the-art research on green computing, energy efficiency, and sustainability in the context of clouds, data centers, edge computing, and IoT. | Dozent: Prof. Tevfik Kosar | |
| Informatik, Ethik, Gesellschaft | Universität Zürich | Wahlmodul im Bachelor | 3 ECTS | Diese Vorlesung führt in ethische und gesellschaftliche Fragen der Technikentwicklung ein und zeigt deren Relevanz für die Informatik und Digitalisierung auf. | Dozent: Prof. Lorenz Hilty |
| Digitalization and Sustainable Development | Universität Zürich | Wahlmodul im Master | 3 ECTS | The digital transformation involves both opportunities and risks for sustainable development. The course addresses how the digital transformation can help society to face the challenges of sustainable development as reflected in the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It provides an overview of results from the emerging research field "Information and Communication Technology for Sustainability (ICT4S)". | Dozent: Prof. Lorenz Hilty |
| Sustainable Computing | University of Pau and Pays de l'Adour | Wahlmodul im Master Computer Science | 4 ECTS | The objective of this course is to explain the notion of sustainable computing and Green IT, and to understand and practice the main concepts and approaches related to multi-platform energy measurement (PCs, servers, IoT, CPS, mobile), software eco-design, and green data centers and clouds. | Dozent: Dr. Adel Noureddine Artikel: Teaching Green and Sustainable Computing: Challenges and Ideas |
| TU Delft | Wahlmodul im Master Computer Science | 5 ECTS |
| Dozent: Luís Cruz Intro blog article: The Five Dimensions of Sustainable Software Engineering and How Education Can Help! | |
| Green IT | HfT Stuttgart | Wahlmodul im Bachelor Informatik | ? |
| Dozent: Prof. Gerhard Wanner Mitwirkend: envite consulting GmbH |
| Current Development Trends in Environmental Informatics | HTW Berlin | Wahlmodul | ? | The course focuses on teaching students how to develop energy-efficient and environmentally friendly software by optimizing the energy efficiency of software applications by, for example, writing energy-efficient algorithms or optimizing the performance of servers and data centers. For this purpose, the basic concepts of ’Green IT’ are taught, and the Green Coding subfield is addressed. The course is divided into three modular parts: internal lectures, external lectures, and a practical part to manifest the theoretical knowledge. | Mitwirkend: Dennis Maximilian Junger Mehr Informationen: Junger, D., & Wohlgemuth, V. (2023). Design and implementation of a lecture for teaching current green coding approaches and practices at the HTW berlin (pp. 1197–1206). Gesellschaft für Informatik e.V. https://dl.gi.de/handle/20.500.12116/43053 |
|
Spezialisierte Studiengänge zu "Informatik & Nachhaltigkeit"
| Name | Abschluss | Hochschule | Anmerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bachelor of Science | Hochschule Trier | ||
| Bachelor of Science | Universität Würzburg | existiert seit dem Wintersemester 2021/22 | |
| Master of Science | Hochschule Luzern | ||
Master of Science | LUT University (Finnland) + Aalborg University Copenhagen |
| |
Erasmus Mundus Master's Programme Software Engineers for Green Deal | Master of Science | LUT University (Finnland) + University L'Aquila (Italien) + Vrije Universtiteit Amsterdam (Niederlande) | |
Studentische Organisationen im Kontext "Informatik & Nachhaltigkeit"
| Name | Hochschule | Ziele | Projekte | Anmerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hochschulgruppe Freie Software Freies Wissen (FSFW) | TU Dresden |
| tbd. | Existiert seit 2014 |
| #gnuHU | HU Berlin |
|
| Existiert seit 2017 |
| TU Dortmund |
| siehe hier | Existiert seit 2016 | |
| digitalcourage Hochschulgruppe | Bielefeld & Bayreuth |
| ||
Was bräuchte es?
Green Software Foundation: Green software should be part of higher education
https://stateof.greensoftware.foundation/insights/green-software-higher-education/
There is a skills gap right now, where engineers, designers, and user experience researchers with sustainability domain knowledge are desperately needed by the ICT industry and for the sake of the climate. However, many respondents to our SOGS survey expressed that current educational and training materials are woefully inadequate. 68% of respondents said more resources would help them and their employers implement green software.
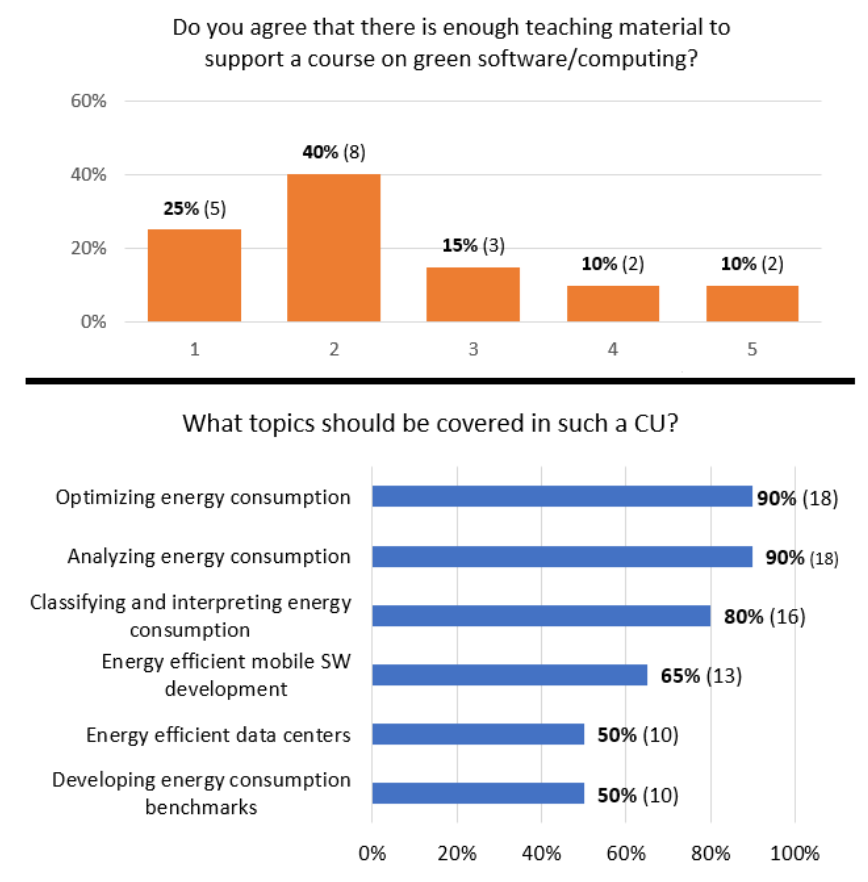
Paper "Bringing Green Software to Computer Science Curriculum: Perspectives from Researchers and Educators"
Saraiva, J., Zong, Z., & Pereira, R. (2021). Bringing Green Software to Computer Science Curriculum: Perspectives from Researchers and Educators. Proceedings of the 26th ACM Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education V. 1, 498–504. https://doi.org/10.1145/3430665.3456386
- "While research in green software is rapidly increasing, several recent studies with software engineers show that they still miss techniques and tools to develop greener software"
- "In fact, all those recent studies show that academia should not only advance state-of-the-art research in green software design, but also educate software engineers towards greener software development. Obviously, this education is best provided from the very beginning of a software engineer career. Unfortunately, today’s undergraduate computer science (CS) education often fails to address our social and environmental responsibility"
- "Question: On a scale of (Highly Disagree) 1-5 (Highly Agree), do you agree that there is enough teaching material available to support a course on green software/computing?"
- "The quickly surging demand for energy efficient computing makes it no longer sufficient for traditional computer science curriculum to train our students with only performance-oriented programming skills and mindset. It is paramount to encourage students to "think green" and write greener code."
Topics covered by the master level course "Green Software Engineering" (University of Minho):
- strategic and aspect oriented programming (compute metrics and transform/refactor source code)
- monitor energy consumption (with RAPL)
- Red smalls + green refactorings (e.g. greeness of Java collections)
- Concept "Energy debt" + monitoring (with E-Debitum plugin for SonarQube)
- fault localization techniques e.g. SPELL)
- Automatic energy-aware program repair
- "We strongly recommend integrating green computing/software modules “early” and “often” to existing courses in a way that enhances what is already taught and that melds naturally in a given course."
Weitere relevante Studien
- Penzenstadler B, Fleischmann A (2011) Teach sustainability in software engineering? In: 2011 24th IEEE-CS Conference on Software Engineering Education and Training (CSEE&T). IEEE, pp 454–458 82.
- Issa T, Issa T, Chang V (2014) Sustainability and green it education: practice for incorporating in the Australian higher education curriculum. Int J Sustain Educ 9(2):19–30 81.
- Pang, C., Hindle, A., Adams, B., & Hassan, A. E. (2016). What Do Programmers Know about Software Energy Consumption? IEEE Software, 33(3), 83–89. https://doi.org/10.1109/MS.2015.83
- Torre, D., Procaccianti, G., Fucci, D., Lutovac, S., & Scanniello, G. (2017). On the Presence of Green and Sustainable Software Engineering in Higher Education Curricula. 2017 IEEE/ACM 1st International Workshop on Software Engineering Curricula for Millennials (SECM), 54–60. https://doi.org/10.1109/SECM.2017.4
- Gil D, Fernández-Alemán JL, Trujillo J, García-Mateos G, Luján-Mora S, Toval A (2018) The effect of green software: a study of impact factors on the correctness of software. Sustainability 10(10):3471
Junger, D., & Wohlgemuth, V. (2023). Design and implementation of a lecture for teaching current green coding approaches and practices at the HTW berlin (pp. 1197–1206). Gesellschaft für Informatik e.V. https://dl.gi.de/handle/20.500.12116/43053
Junger, D., Westing, M., Freitag, C. P., Guldner, A., Mittelbach, K., Obergöker, K., Weber, S., Naumann, S., & Wohlgemuth, V. (2024). Potentials of green coding—Findings and recommendations for industry, education and science—Extended paper (arXiv:2402.18227). arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2402.18227